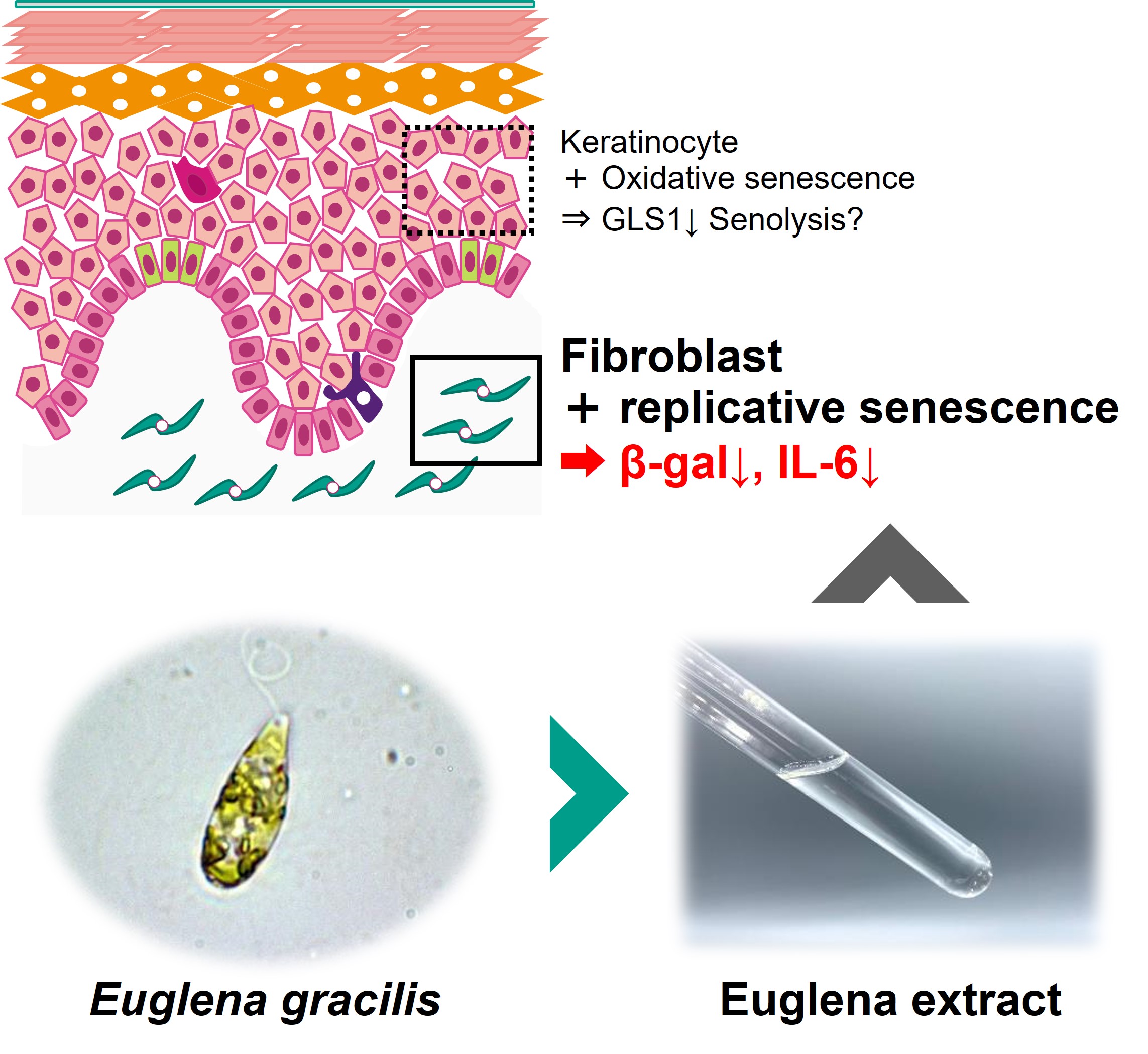
The Effect of Euglena Extract on Senescent Human Skin Fibroblasts
Human skin, the primary barrier protecting the body from external environments, shows signs of aging such as wrinkles, sagging, and spots with age. One contributing factor to these aging signs is the senescence of skin components like keratinocytes and fibroblasts. This study focuses on the aging phenomenon of skin cells, using senescent cells produced by replicating human dermal fibroblasts, to examine the effects of an extract derived from the microalga Euglena (Euglena Extract EX) on aging.
Euglena, a microalga combining characteristics of both plants and animals, is industrially used in health foods and cosmetic ingredients. Previous studies have reported that Euglena extract reduces the expression of aging-related genes in an aging model using human epidermal keratinocytes treated with hydrogen peroxide.
In our study, the senescent cells, created by replicating human dermal fibroblasts, exhibited higher β-galactosidase activity, a marker of aging, and increased expression of the IL-6 gene, known as a senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP), compared to younger cells with fewer replications. However, upon addition and cultivation with Euglena extract, a decrease in β-galactosidase activity and IL-6 gene expression was observed, suggesting that Euglena extract could inhibit cellular aging.
The results of this study indicate that Euglena extract, derived from microalgae, could be a promising intervention method against skin cell aging. Furthermore, based on previous research, Euglena might affect multiple types of skin cells and various aging phenomena caused by different factors (like oxidative stress and replicative aging), and further research is anticipated to elucidate the specific mechanisms of action.
The results of this study were presented at the 46th Annual Meeting of the Molecular Biology Society of Japan held on December 6-8, 2023.
Research Content and Results
The addition of Euglena Extract EX to aged human dermal fibroblasts confirmed the suppression of aging phenomena.
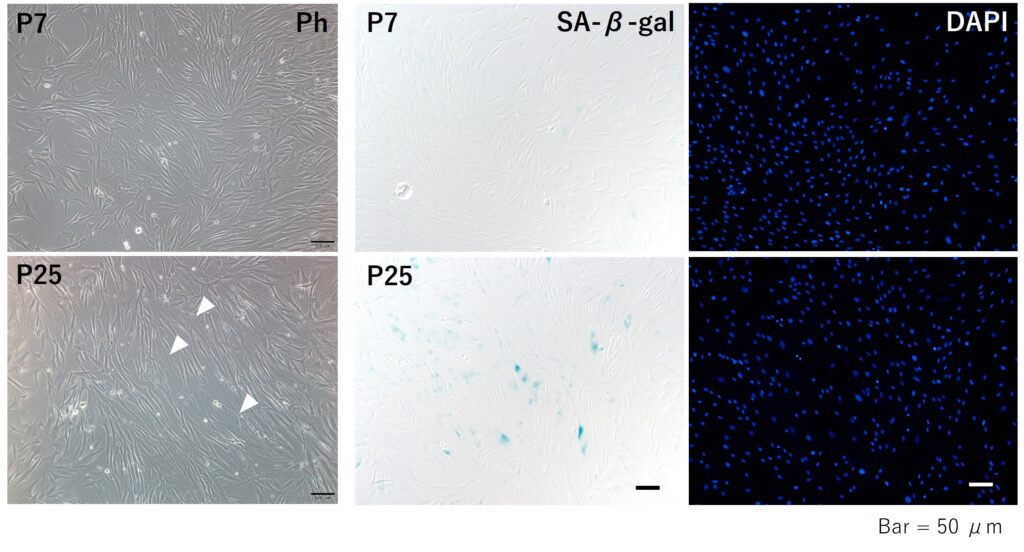
Human dermal fibroblasts were cultured and aged through multiple replications. In these artificially aged cells, enlarged cells, a characteristic of senescent cells, were observed (Figure 1, white arrowheads in Ph). Furthermore, when β-galactosidase activity, a marker of aging, was detected by staining, a higher presence of β-galactosidase-positive cells, appearing blue, was found in the aged cells compared to younger cells with fewer replications (Figure 1, β-gal). These results indicate that we have successfully created artificially aged human dermal fibroblasts through replication.
The artificially aged cells were cultivated for three days with the addition of Euglena Extract EX, and β-galactosidase activity, a marker of aging, was detected using fluorescence. The fluorescence intensity was measured by flow cytometry. The results showed that, compared to younger cells, the aged cells (Figure 2, Aged Cells EX 0%) exhibited increased β-galactosidase activity. However, a decrease in β-galactosidase activity was observed with the addition of Euglena Extract EX (Figure 2).
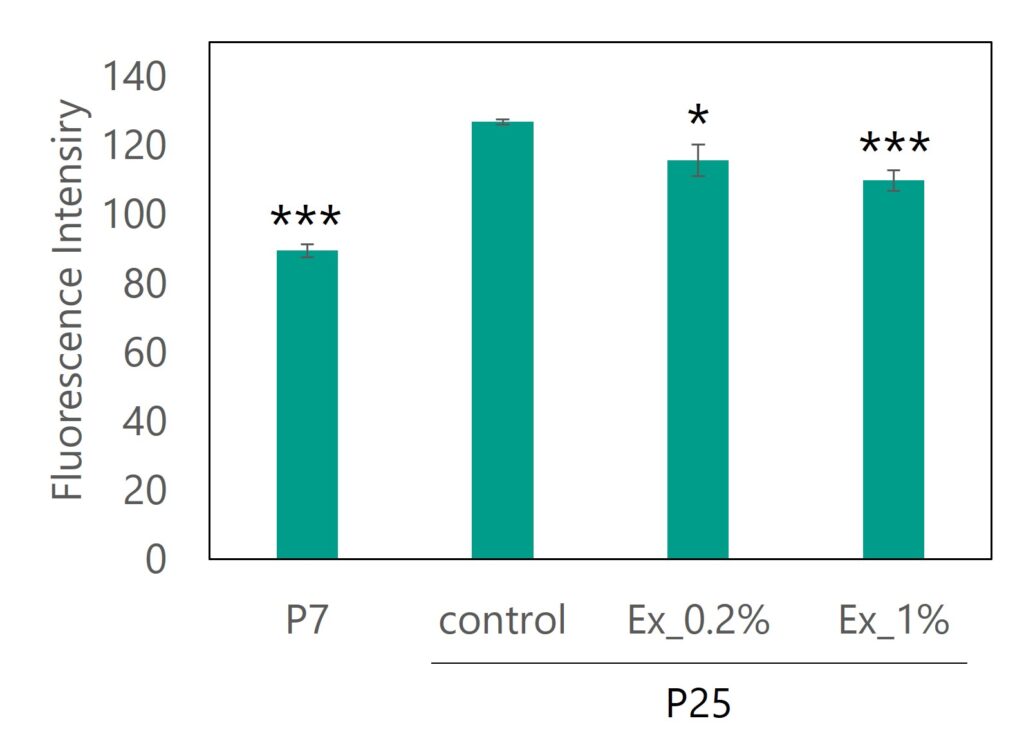
Dunnett tst vs P25_control, p<0.1“+”, p<0.05 “*”, p<0.01”**” , p<0.001”***”, n=3
Additionally, the gene expression of IL-6 and IL-1α, types of senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) factors, was examined. It was found that in aged cells (Figure 3, Aged Cells EX 0%), their expression increased compared to younger cells. However, with the addition of Euglena Extract EX, a decrease in the gene expression of IL-6 and IL-1α was observed compared to the untreated aged cells (Figure 3, Aged Cells EX 0%).
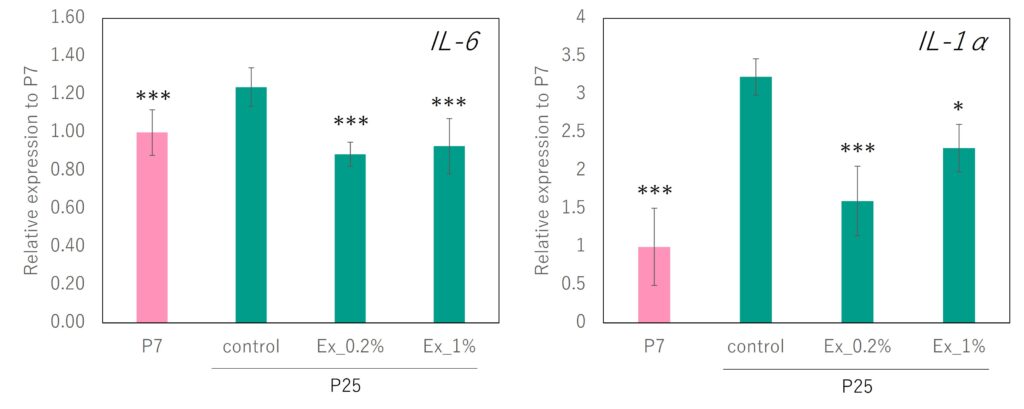
Dunnett vs P25_control, p<0.1“+”, p<0.05 “*”, p<0.01”**” , p<0.001”***”, n=4
From the above results, it is suggested that Euglena Extract EX can suppress the aging phenomena in human dermal fibroblasts.
Furthermore, previous research has indicated that Euglena Extract EX is also effective in cells aged by oxidative stress induced using hydrogen peroxide in human epidermal keratinocytes. Therefore, it is expected that Euglena Extract EX may contribute to improving aging phenomena originating from multiple causes (such as oxidative stress and replicative aging) in various types of skin cells.
